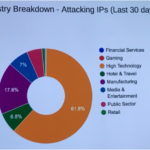
 TAIPEI (Taiwan News)—Most denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks launched by hackers from Feb. 15 to March 14, 2017 in Taiwan targeted the high-tech industry, according to statistics compiled by leading global content delivery network provider Akamai Technologies. Industries in Taiwan that were most severely attacked by hackers were the high technology industry (61.8 percent), manufacturing industry (17.6 percent) and the financial services industry (7 percent), according to statistics compiled by Akamai’s intelligent platform that delivers 30 percent of the global Internet traffic. Industries in Taiwan under DDoS attacks from February 15 to March 14, 2017. (Taiwan News) The majority of the hacks were launched from IP addresses in Taiwan, followed by Alabama in the U.S., and Brazil. “It is often a misconception that most attacks are launched from abroad,” said Akamai’s Security Business Unit director Amol Mathur. “Attacks are coming both domestic and outside.” The premium CDN provider works customizes solutions for clients from different industries in Taiwan, including hospitality, banking, travel and airline services. Taiwan’s financial institutes are still recovering from a cybersecurity scare last month, in which 15 banks received threats from an anonymous hacker group to shell out 10 Bitcoins each (equivalent to US$10,466), or brace themselves for DDoS attacks that would compromise their server systems. DDoS attacks launched by hackers often compromise institute’s servers data processing capacity by delivering a sudden deluge of data that overtakes bandwidth resources, for instance if the company server bandwidth only allows 10 Gigabyte per second (Gbps) of capacity it can be paralyzed by a 100 Gbps attack. Hackers might use DDoS as a distraction to conceal other malign operations, such as stealing personal information or credential theft, added Mathur. Industries affected by hacker attacks vary monthly, depending on whether there is a major geopolitical event, said Mathur. For instance global hacker group Anonymous took down the London Stock Exchange system for two hours as part of its campaign against global central banks in June 2016. Mathur advised banks should not heed hacker demands to pay ransom. “In real life you would not pay ransom, so why would you pay hackers,” he said. The cybersecurity expert noted a rise in DDoS attacks globally during the fourth quarter of 2016, and pointed out DDoS attacks data size was increasing exponentially every quarter. Globally, attacks over 100 Gbps jumped 140 percent year-on-year during 4Q16, with the largest-size attack recorded reaching 517 Gbps, according to the Akamai “Fourth quarter 2016 State of the Internet/Security Report.” Mathur noted the cause of increased DDoS attacks was partly due to easy access for people to rent bots online, for as cheap as US$10 by going to a site and simply keying in the website address. Hackers can generate a monthly income of US$180,000 to US$200,000 from bot rentals. It remains extremely difficult for law enforcement agencies from a single country to track down hackers that spread the attacks launched by rented bots around the globe, and hide behind the protection of anonymity offered by the dark web. Additionally, the preferred Bitcoin currency used for business transactions by hackers is hard to trace to an IP address, explained Mathur. Introduction of mobile devices, mobile payment, IP surveillance cameras and emerging Internet of Things (IoT) trends introduce new cybersecurity vulnerabilities as hackers can utilize attacks through large number of connected devices. The Mirai bot for instance exposed vulnerabilities in the default user administrator name and passwords used by thousands of connected IP surveillance cameras and their DVR worldwide, said Mathur. He urged the IoT industry to form a joint standard, and for countries to start implementing regulations that set cybersecurity standards for connected devices. Hackers are also finding ways to target vulnerabilities in smartphone application programming interface (API) to obtain credentials, and data from mobile transactions. Apple Pay and some other mobile payment technologies periodically publish white papers announcing how it is securing data, but are mostly for tech savvy readers, said Mathur. One way consumers can safeguard credit card transactions is to check if the online shopping sites or App they use have The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), noted Mathur. The proprietary information security standard launched nearly a decade ago by major credit card companies Visa, MasterCard, American Express, JCB and others follows a stringent standard and heavily fines companies that do not follow its compliance. Source: http://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/3117326
TAIPEI (Taiwan News)—Most denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks launched by hackers from Feb. 15 to March 14, 2017 in Taiwan targeted the high-tech industry, according to statistics compiled by leading global content delivery network provider Akamai Technologies. Industries in Taiwan that were most severely attacked by hackers were the high technology industry (61.8 percent), manufacturing industry (17.6 percent) and the financial services industry (7 percent), according to statistics compiled by Akamai’s intelligent platform that delivers 30 percent of the global Internet traffic. Industries in Taiwan under DDoS attacks from February 15 to March 14, 2017. (Taiwan News) The majority of the hacks were launched from IP addresses in Taiwan, followed by Alabama in the U.S., and Brazil. “It is often a misconception that most attacks are launched from abroad,” said Akamai’s Security Business Unit director Amol Mathur. “Attacks are coming both domestic and outside.” The premium CDN provider works customizes solutions for clients from different industries in Taiwan, including hospitality, banking, travel and airline services. Taiwan’s financial institutes are still recovering from a cybersecurity scare last month, in which 15 banks received threats from an anonymous hacker group to shell out 10 Bitcoins each (equivalent to US$10,466), or brace themselves for DDoS attacks that would compromise their server systems. DDoS attacks launched by hackers often compromise institute’s servers data processing capacity by delivering a sudden deluge of data that overtakes bandwidth resources, for instance if the company server bandwidth only allows 10 Gigabyte per second (Gbps) of capacity it can be paralyzed by a 100 Gbps attack. Hackers might use DDoS as a distraction to conceal other malign operations, such as stealing personal information or credential theft, added Mathur. Industries affected by hacker attacks vary monthly, depending on whether there is a major geopolitical event, said Mathur. For instance global hacker group Anonymous took down the London Stock Exchange system for two hours as part of its campaign against global central banks in June 2016. Mathur advised banks should not heed hacker demands to pay ransom. “In real life you would not pay ransom, so why would you pay hackers,” he said. The cybersecurity expert noted a rise in DDoS attacks globally during the fourth quarter of 2016, and pointed out DDoS attacks data size was increasing exponentially every quarter. Globally, attacks over 100 Gbps jumped 140 percent year-on-year during 4Q16, with the largest-size attack recorded reaching 517 Gbps, according to the Akamai “Fourth quarter 2016 State of the Internet/Security Report.” Mathur noted the cause of increased DDoS attacks was partly due to easy access for people to rent bots online, for as cheap as US$10 by going to a site and simply keying in the website address. Hackers can generate a monthly income of US$180,000 to US$200,000 from bot rentals. It remains extremely difficult for law enforcement agencies from a single country to track down hackers that spread the attacks launched by rented bots around the globe, and hide behind the protection of anonymity offered by the dark web. Additionally, the preferred Bitcoin currency used for business transactions by hackers is hard to trace to an IP address, explained Mathur. Introduction of mobile devices, mobile payment, IP surveillance cameras and emerging Internet of Things (IoT) trends introduce new cybersecurity vulnerabilities as hackers can utilize attacks through large number of connected devices. The Mirai bot for instance exposed vulnerabilities in the default user administrator name and passwords used by thousands of connected IP surveillance cameras and their DVR worldwide, said Mathur. He urged the IoT industry to form a joint standard, and for countries to start implementing regulations that set cybersecurity standards for connected devices. Hackers are also finding ways to target vulnerabilities in smartphone application programming interface (API) to obtain credentials, and data from mobile transactions. Apple Pay and some other mobile payment technologies periodically publish white papers announcing how it is securing data, but are mostly for tech savvy readers, said Mathur. One way consumers can safeguard credit card transactions is to check if the online shopping sites or App they use have The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), noted Mathur. The proprietary information security standard launched nearly a decade ago by major credit card companies Visa, MasterCard, American Express, JCB and others follows a stringent standard and heavily fines companies that do not follow its compliance. Source: http://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/3117326
Originally posted here:
Taiwan high-tech industry hardest hit by DDoS attacks in last 30 days


 TAIPEI (Taiwan News)—Most denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks launched by hackers from Feb. 15 to March 14, 2017 in Taiwan targeted the high-tech industry, according to statistics compiled by leading global content delivery network provider Akamai Technologies. Industries in Taiwan that were most severely attacked by hackers were the high technology industry (61.8 percent), manufacturing industry (17.6 percent) and the financial services industry (7 percent), according to statistics compiled by Akamai’s intelligent platform that delivers 30 percent of the global Internet traffic. Industries in Taiwan under DDoS attacks from February 15 to March 14, 2017. (Taiwan News) The majority of the hacks were launched from IP addresses in Taiwan, followed by Alabama in the U.S., and Brazil. “It is often a misconception that most attacks are launched from abroad,” said Akamai’s Security Business Unit director Amol Mathur. “Attacks are coming both domestic and outside.” The premium CDN provider works customizes solutions for clients from different industries in Taiwan, including hospitality, banking, travel and airline services. Taiwan’s financial institutes are still recovering from a cybersecurity scare last month, in which 15 banks received threats from an anonymous hacker group to shell out 10 Bitcoins each (equivalent to US$10,466), or brace themselves for DDoS attacks that would compromise their server systems. DDoS attacks launched by hackers often compromise institute’s servers data processing capacity by delivering a sudden deluge of data that overtakes bandwidth resources, for instance if the company server bandwidth only allows 10 Gigabyte per second (Gbps) of capacity it can be paralyzed by a 100 Gbps attack. Hackers might use DDoS as a distraction to conceal other malign operations, such as stealing personal information or credential theft, added Mathur. Industries affected by hacker attacks vary monthly, depending on whether there is a major geopolitical event, said Mathur. For instance global hacker group Anonymous took down the London Stock Exchange system for two hours as part of its campaign against global central banks in June 2016. Mathur advised banks should not heed hacker demands to pay ransom. “In real life you would not pay ransom, so why would you pay hackers,” he said. The cybersecurity expert noted a rise in DDoS attacks globally during the fourth quarter of 2016, and pointed out DDoS attacks data size was increasing exponentially every quarter. Globally, attacks over 100 Gbps jumped 140 percent year-on-year during 4Q16, with the largest-size attack recorded reaching 517 Gbps, according to the Akamai “Fourth quarter 2016 State of the Internet/Security Report.” Mathur noted the cause of increased DDoS attacks was partly due to easy access for people to rent bots online, for as cheap as US$10 by going to a site and simply keying in the website address. Hackers can generate a monthly income of US$180,000 to US$200,000 from bot rentals. It remains extremely difficult for law enforcement agencies from a single country to track down hackers that spread the attacks launched by rented bots around the globe, and hide behind the protection of anonymity offered by the dark web. Additionally, the preferred Bitcoin currency used for business transactions by hackers is hard to trace to an IP address, explained Mathur. Introduction of mobile devices, mobile payment, IP surveillance cameras and emerging Internet of Things (IoT) trends introduce new cybersecurity vulnerabilities as hackers can utilize attacks through large number of connected devices. The Mirai bot for instance exposed vulnerabilities in the default user administrator name and passwords used by thousands of connected IP surveillance cameras and their DVR worldwide, said Mathur. He urged the IoT industry to form a joint standard, and for countries to start implementing regulations that set cybersecurity standards for connected devices. Hackers are also finding ways to target vulnerabilities in smartphone application programming interface (API) to obtain credentials, and data from mobile transactions. Apple Pay and some other mobile payment technologies periodically publish white papers announcing how it is securing data, but are mostly for tech savvy readers, said Mathur. One way consumers can safeguard credit card transactions is to check if the online shopping sites or App they use have The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), noted Mathur. The proprietary information security standard launched nearly a decade ago by major credit card companies Visa, MasterCard, American Express, JCB and others follows a stringent standard and heavily fines companies that do not follow its compliance. Source: http://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/3117326
TAIPEI (Taiwan News)—Most denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks launched by hackers from Feb. 15 to March 14, 2017 in Taiwan targeted the high-tech industry, according to statistics compiled by leading global content delivery network provider Akamai Technologies. Industries in Taiwan that were most severely attacked by hackers were the high technology industry (61.8 percent), manufacturing industry (17.6 percent) and the financial services industry (7 percent), according to statistics compiled by Akamai’s intelligent platform that delivers 30 percent of the global Internet traffic. Industries in Taiwan under DDoS attacks from February 15 to March 14, 2017. (Taiwan News) The majority of the hacks were launched from IP addresses in Taiwan, followed by Alabama in the U.S., and Brazil. “It is often a misconception that most attacks are launched from abroad,” said Akamai’s Security Business Unit director Amol Mathur. “Attacks are coming both domestic and outside.” The premium CDN provider works customizes solutions for clients from different industries in Taiwan, including hospitality, banking, travel and airline services. Taiwan’s financial institutes are still recovering from a cybersecurity scare last month, in which 15 banks received threats from an anonymous hacker group to shell out 10 Bitcoins each (equivalent to US$10,466), or brace themselves for DDoS attacks that would compromise their server systems. DDoS attacks launched by hackers often compromise institute’s servers data processing capacity by delivering a sudden deluge of data that overtakes bandwidth resources, for instance if the company server bandwidth only allows 10 Gigabyte per second (Gbps) of capacity it can be paralyzed by a 100 Gbps attack. Hackers might use DDoS as a distraction to conceal other malign operations, such as stealing personal information or credential theft, added Mathur. Industries affected by hacker attacks vary monthly, depending on whether there is a major geopolitical event, said Mathur. For instance global hacker group Anonymous took down the London Stock Exchange system for two hours as part of its campaign against global central banks in June 2016. Mathur advised banks should not heed hacker demands to pay ransom. “In real life you would not pay ransom, so why would you pay hackers,” he said. The cybersecurity expert noted a rise in DDoS attacks globally during the fourth quarter of 2016, and pointed out DDoS attacks data size was increasing exponentially every quarter. Globally, attacks over 100 Gbps jumped 140 percent year-on-year during 4Q16, with the largest-size attack recorded reaching 517 Gbps, according to the Akamai “Fourth quarter 2016 State of the Internet/Security Report.” Mathur noted the cause of increased DDoS attacks was partly due to easy access for people to rent bots online, for as cheap as US$10 by going to a site and simply keying in the website address. Hackers can generate a monthly income of US$180,000 to US$200,000 from bot rentals. It remains extremely difficult for law enforcement agencies from a single country to track down hackers that spread the attacks launched by rented bots around the globe, and hide behind the protection of anonymity offered by the dark web. Additionally, the preferred Bitcoin currency used for business transactions by hackers is hard to trace to an IP address, explained Mathur. Introduction of mobile devices, mobile payment, IP surveillance cameras and emerging Internet of Things (IoT) trends introduce new cybersecurity vulnerabilities as hackers can utilize attacks through large number of connected devices. The Mirai bot for instance exposed vulnerabilities in the default user administrator name and passwords used by thousands of connected IP surveillance cameras and their DVR worldwide, said Mathur. He urged the IoT industry to form a joint standard, and for countries to start implementing regulations that set cybersecurity standards for connected devices. Hackers are also finding ways to target vulnerabilities in smartphone application programming interface (API) to obtain credentials, and data from mobile transactions. Apple Pay and some other mobile payment technologies periodically publish white papers announcing how it is securing data, but are mostly for tech savvy readers, said Mathur. One way consumers can safeguard credit card transactions is to check if the online shopping sites or App they use have The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), noted Mathur. The proprietary information security standard launched nearly a decade ago by major credit card companies Visa, MasterCard, American Express, JCB and others follows a stringent standard and heavily fines companies that do not follow its compliance. Source: http://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/3117326